
栏目简介:CELL官网 Cell Picture Show(细胞照片秀)栏目(http://www.cell.com/pictureshow),由卡尔蔡司赞助支持,不定期地为大家分享细胞、发育和分子生物学中获得的各种引人注目的照片,让大家欣赏到前沿研究中的美丽图像。
2016年最佳图片展示
希望进入2017年,伴随着技术的进步可以有更美丽更迷人的图像分享给大家。
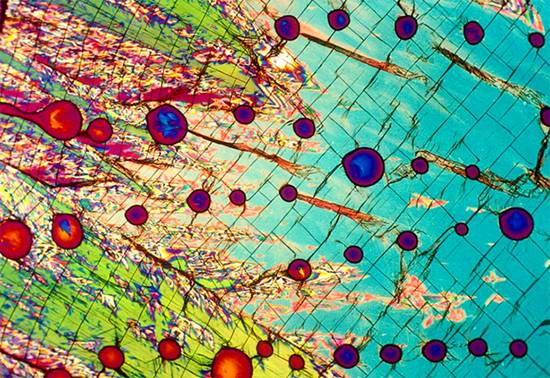
Mike Davidson’s Legacy
Mike Davidson, Florida State University, National High Magnetic Field Laboratory
Image of vodka taken by Michael W. Davidson. In the 1990s, Michael W. Davidson pioneered new photo microscopy techniques in his laboratory at Florida State University (FSU). For this image, vodka was crystallized and viewed under a polarized light microscope. Image courtesy of www.bevshots.com.
迈克戴维森的遗作
迈克戴维森:佛罗里达州立大学-国家强磁场实验室-著名显微镜专家,2015年逝世。
在20世纪九十年代,Michael W. Davidson在佛罗里达州立大学(FSU)他的实验室里开创了一项新的显微镜成像技术,上图为伏特加结晶在偏振光显微镜下的图像。图片由www.bevshots.com.提供。
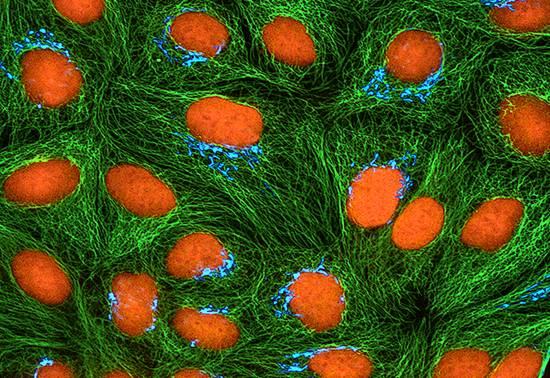
To the Golgi We Go
Thomas Deerinck and Mark Ellisman, NCMIR, UCSD
Image: Confocal microscopy image of cultured HeLa cells expressing CFP targeted to the Golgi Apparatus, made by Michael Davidson. Cells were immunolabeled for tubulin (green) and counterstained with propidium iodide to label DNA (orange). The Davidson Lab made thousands of conventional fluorophores constructs such as this CFP, and most are available from the nonprofit depository Addgene.
To the Golgi We Go
Thomas Deerinck和Mark Ellisman,NCMIR,UCSD
共聚焦显微镜图像——Michael Davidson制造的在HeLa细胞中表达CFP的靶向高尔基体。将细胞免疫荧光标记微管蛋白(绿色),并用PI复染色标记DNA(橙色)。戴维森实验室已经制造出了上千种的常规荧光结构例如此图的CFP,并且大多数都可以向非营利保藏者Addgene获取。

Signals 2011
C. E. B. Reas and Ben Fry
Cell behavior is controlled by interconnected proteins operating in a network to actively transmit instructions. These networks become dysfunctional in cancerous cells. In this image, each graphical cluster represents signals between networked proteins in a cancer cell as they change over time. Individual arcs are signals from one protein to another; the size of an arc corresponds to the magnitude of the signal.
信号2011
CEB Reas和Ben Fry
互相连接的蛋白通过在它们的网络中主动连接传递信号从而控制细胞的行为,而在癌细胞中,这些网络存在着功能障碍。此图中的团状图形表示的是在一个癌细胞中网络化蛋白之间的信号在随着时间发生变化。单个的弧形是从一个蛋白到另一个蛋白的信号;弧形的大小对应着信号的强弱。
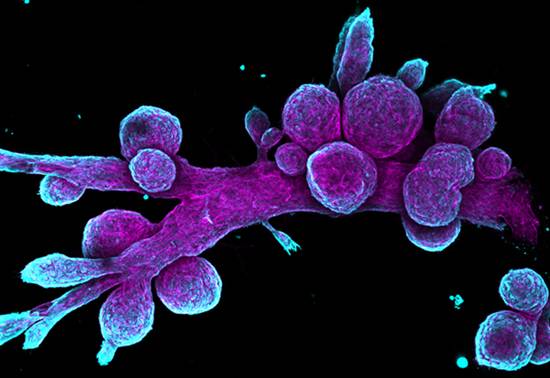
Duct, Duct, Goose
Daniel H. Miller, Dexter X. Jin, Piyush B. Gupta
Whitehead Institute and Koch Institute at MIT
Chasing Down Answers in Developmental Biology (原文地址)
Watch out for foul play! By examining the normal growth of biological structures, scientists figure out how developmental processes are perturbed in cancer and other diseases.
Image: This image shows the architecture (purple) and cell types (cyan) in the human mammary gland. The round lobes seen here are responsible for production of milk, which then travels through the duct to the nipple in a mature female. Using this model as a starting point, biologists can now begin to study how genetic and chemical perturbations can disrupt tissue development and cause disease.
Duct, Duct, Goose
Daniel H. Miller,Dexter X. Jin,Piyush B. Gupta
麻省理工的Whitehead 学院和Koch 学院
“在发育生物学中追寻到的答案”
注意犯规的游戏!通过检查生物结构的正常生长,科学家清楚了发育过程在癌症和其他疾病中是如何被干扰破坏的。
此图显示的是人类乳腺的体系结构(紫色)和细胞类型(青绿色)。图中的圆形组织负责产生奶,然后通过管道进入成熟女性的乳头。使用这个模型作为起点,生物学家现在可以开始研究遗传和化学因素是怎样干扰了组织的发育和疾病的产生。

Suit Your Cell
Asha K. Patel, Daniel G. Anderson, Robert S. Langer, Morgan R. Alexander, Chris N. Denning, Martyn C. Davies
”Koch Institute at MIT and University of Nottingham”
Designing Custom Biomaterials (原文地址)
Developing materials for biotechnology is not a one-size-fits-all approach. Different cell types behave in different ways depending on the materials they interact with.
Image: This composite image shows how heart cells (fibrous images, e.g., row 2, column 1) and stem cells (spotted images, e.g., row 1, column 3) respond to various synthetic polymers deposited onto microscopic arrays. After testing hundreds of chemical combinations, the most promising candidates are selected to develop tailor-made materials for biomedical research and clinical applications.
为您量身定制细胞
Asha K. Patel,Daniel G. Anderson,Robert S. Langer,Morgan R. Alexander,Chris N. Denning,Martyn C. Davies
麻省理工和诺丁汉大学的科赫研究所
“设计定制生物材料”
开发生物技术材料不是一件一劳永逸的事。不同的细胞类型根据与他们相互作用的材料会做出不同方式的表现。
该图是一副合并图像,显示的是心脏细胞(纤维状图像,例如第2行第1列)和干细胞(点状图像,例如第1行第3列)对于沉积在微观阵列上的各种合成聚合物变现出的反应。在测试了数百种化学组合之后,最有希望的组合将被用于开发生物医学研究和临床应用上的定制材料。
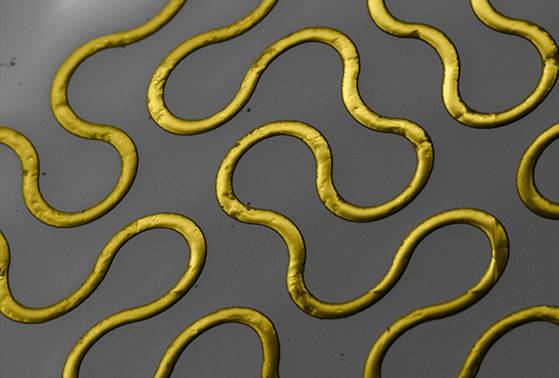
Nerves of Gold
Jonathan K. Tsosie, Omar F. Khan, Daniel G. Anderson, Robert S. Langer Koch Institute at MIT
New Potential for Regenerative Medicine
This stretchable device stands in for the nervous system after neural separation to provide electronic stimulation to muscles, promoting contraction and preventing atrophy.
Image: The circuitous path of gold in this image may seem random, but it is actually a fractal pattern designed to improve the elasticity of hard-metal components used in restorative bionics. In addition to keeping muscles active while nerves regenerate, this biocompatible circuit board will collect data about the repair process, increasing capacity for both treatment and understanding.
金子的神经
Jonathan K.Tosie,Omar F.Khan,Daniel G.Anderson ,Robert S.Langer Koch Institute at MIT
“再生医学的新潜力”
这种可伸展装置在神经分离后代表神经系统,以向肌肉提供电子刺激,促进收缩和预防萎缩。
图像:这个图像中的金子的迂回路径可能看起来是随机的,但它实际上是一个分形图案,旨在提高修复性仿生学中使用的硬金属部件的弹性。除了在神经再生时保持肌肉活动,该生物相容性电路板将收集关于修复过程的数据,增加治疗和理解的能力。
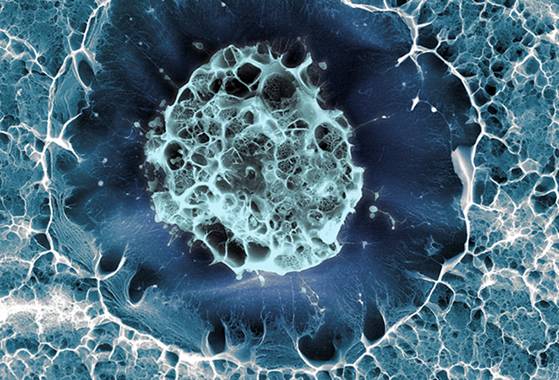
Stem Education
Sílvia A Ferreira, Cristina Lopo, Eileen Gentleman
King's College London
Imagine the Possibilities
What do you want to be when you grow up? This is the question every young stem cell must ask itself before it differentiates. But as with any development, outside influences are not to be overlooked.
Image: The stem cell seen here has been cryogenically frozen in a hydrogel matrix, designed to mimic the cell’s native environment in the bone marrow. Researchers are studying the interactions between the cell and its surroundings—and nurturing new understandings of how nature works.
This image appears in the Koch Institute Public Galleries as part of a partnership between the Koch Institute and Wellcome Images, a London-based world leader in the collection of biomedical images. To learn more about Wellcome Images, visit their website at: http://wellcomeimages.org/.
SílviaAFerreira,Cristina Lopo,Eileen绅士
伦敦国王学院
可能性想象
你长大后想做什么?这是每个年轻干细胞在分化之前必须问自己的问题。但与任何发展一样,外部影响不容忽视。
图像:这里看到的干细胞已经在水凝胶基质中低温冷冻,设计为模拟细胞在骨髓中的天然环境。研究人员正在研究细胞与其周围环境之间的相互作用 - 并且培育对自然如何工作的新认识。
这张图片出现在科赫研究所公共图书馆,作为Koch研究所和伦敦的世界领先的生物医学图像集合之一Wellcome图片之间的合作伙伴关系的一部分。要了解更多关于Wellcome图片,请访问他们的网站:http://wellcomeimages.org /。
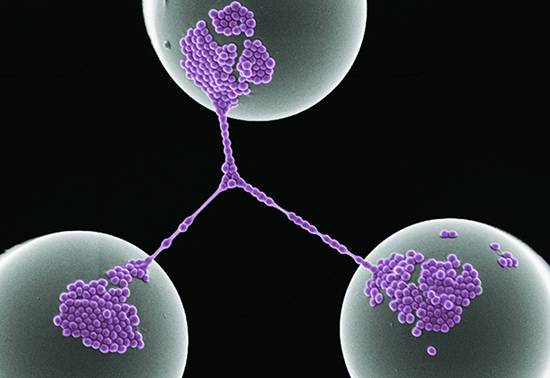
Bacterial Networking
Zeinab Jahed
University of California, Berkeley
This is a false-colored scanning electron microscope image of Staphylococcus Aureus bacterial cells forming networks on top of poly-dimethyl-siloxane (PDMS) micro-posts (top-down view).
细菌网络
加利福尼亚
大学伯克利分校
这是在聚二甲基硅氧烷(PDMS)微柱(自顶向下视图)顶部形成网络的金黄色葡萄球菌细菌的假彩色扫描电子显微镜图像。
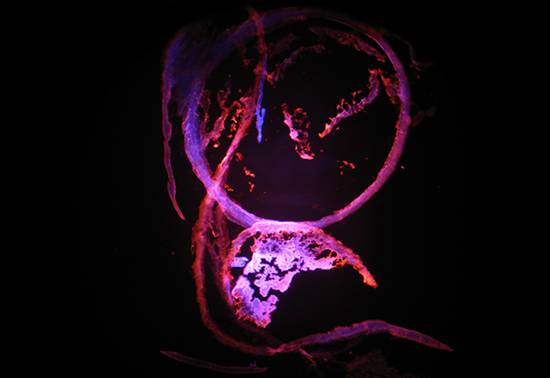
Dreamcatcher
Marie Kelly-Worde
Ball State University
The image is of mouse eye tissue. Florescence is provided by Rose-Bengal and DAPI. Damaged tissue is stained by the Rose-Bengal, while healthy tissue is stained by DAPI. The image was acquired at 100x magnification.
追梦者
Marie Kelly-Worde
球州立大学
图片是鼠眼组织。花期由Rose-Bengal和DAPI提供。损伤的组织被玫瑰 - 孟加拉染色,而健康组织被DAPI染色。在100x放大率下获取图像。

Light Trails of Receptor Tyrosine Kinase EphA2
Thomas Newport
University of Oxford
This image shows simulated dynamics of the ectodomain of the receptor tyrosine kinase EphA2 (shown as glowing lines) as well as different conformations that highlight the possible movement of this receptor relative to the membrane surface. Simulated in GROMACS, rendered in Blender 3D.
受体酪氨酸激酶EphA2的光径
托马斯·纽波特
牛津大学
该图显示受体酪氨酸激酶EphA2的胞外域的模拟动力学(显示为发光线)以及突出该受体相对于膜表面的可能运动的不同构象。在GROMACS中模拟,在Blender 3D中渲染。
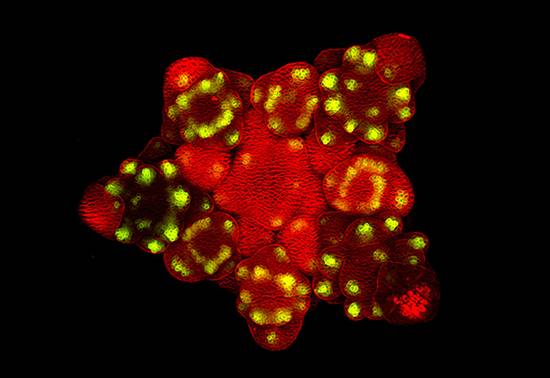
Everything Is Coming Up Arabidopsis
Nat Prunet, Caltech
The mouse ear crest, or thale crest, is a small flowering plant native to much of Europe and Asia. Arabidopsis thalianahas long served as a popular model organism in plant biology and genetics as a complex multicellular eukaryote with a short lifecycle and relatively small genome (~135 megabase pairs [Mbp]). Arabidopsis thaliana was the first plant to have its genome completely sequenced and remains an important research tool for understanding the molecular biology of plant behaviors, such as flower development and light sensitivity.
Image: Confocal image of an old inflorescence of the Arabidopsis apetala1 mutant. Green fluorescence marks the expression of the DORNROSCHEN-LIKE gene in the founder cells of floral organs. Plasma membranes were stained with FM4-64 (red).
onecut都来了拟南芥
Nat Prunet,Caltech
小鼠耳嵴或thale冠,是一个小的开花植物当地对欧洲和亚洲的大部分。拟南芥长期以来作为具有短生命周期和相对小的基因组(〜13兆碱基对[Mbp])的复杂多细胞真核生物在植物生物学和遗传学中作为流行模式生物体。拟南芥是第一个使其基因组完全测序的植物,并且是理解植物行为的分子生物学(例如花发育和光敏感性)的重要研究工具。
图像:拟南芥APETALA1突变行业释义体育的旧花序的共焦图像。绿色荧光标记DORNROSCHEN般的基因在花器官起始细胞中的表达。用FM4-64(红色)染色血浆膜。
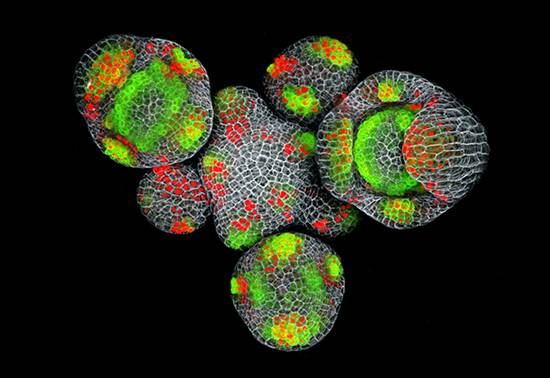
Make Like an Arabidopsis and Leave
Nat Prunet, Caltech
Due to the flexibility of its genome, Arabidopsis thaliana has the ability to adapt for survival in various environmental conditions. Not only can it endure the heat and droughts of northern Africa, Arabidopsis also thrives in the cold of the central Asian highlands and temperate zones in Europe. Depending on the region, it adapts or can display extensive foliage or appear small and fragile. Investigating the genetic basis and mode of adaptation has important implications for global climate change.
Image: Confocal image of an Arabidopsis inflorescence expressing fluorescent reporters for the expression of theDORNROSCHEN-LIKE gene (DRNL, green) and auxin accumulation (red). Both DRNL and auxin are involved in the initiation of floral organs. Cell walls were stained with propidium iodide (gray).
做一个拟南芥和离开
Nat Prunet,Caltech
由于其基因组的灵活性,拟南芥具有适应在各种环境条件下的存活的能力。不仅能忍受北非的热和干旱,拟南芥也在欧洲中亚高地和温带地区的寒冷中茁壮成长。根据区域,它适应或可以显示广泛的叶子或看起来小而脆弱。
图像:表达用于表达DORNROSCHEN样基因(DRNL,绿色)和生长素积累(红色)的荧光报道分子的拟南芥花序的共焦图像。既DRNL。生长素状语从句:花参与器官的启动细胞壁用碘化丙啶染色(灰色)。
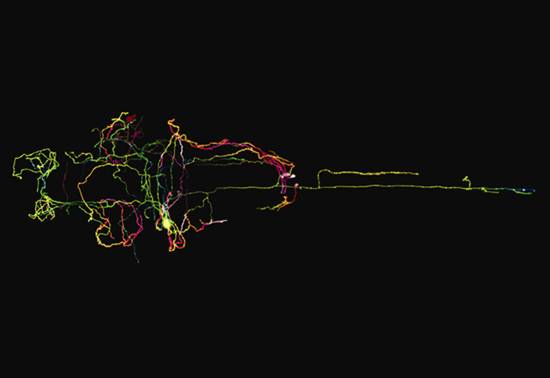
A Single Neuron
Tong Xiao and Beth Carroll. Isacoff Labs. University of California. Berkeley.
A single LC neuron labeled with mCherry in a 4 dpf zebrafish.
单神神元
童晓和贝丝·卡罗尔。Isacoff实验室。加利福尼亚大学。伯克利。
在4dpf斑马鱼中用mCherry标记的单个LC神经元。